Introduction
Wound healing is a complex physiological process that involves various cellular and molecular mechanisms. Oxygen plays a critical role in this process, as it is essential for energy production, cellular function, and tissue repair. Oxygen therapy has emerged as a promising approach to enhance healing by providing optimal oxygen levels to promote tissue repair and regeneration.
Understanding Wound Healing
Wound healing is divided into distinct phases: inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. Oxygen is crucial throughout these stages to support immune responses, stimulate cell growth, and facilitate collagen synthesis. Inadequate oxygen supply can lead to delayed healing, chronic wounds, and increased risk of infections.
Mechanisms of Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy delivers increased levels of oxygen to wound tissues, which can accelerate healing through multiple mechanisms. It enhances cellular metabolism, increases white blood cell activity, promotes angiogenesis (blood vessel formation), and supports collagen synthesis. These combined effects lead to improved tissue repair and faster healing.
Types of Oxygen Therapy for Healing
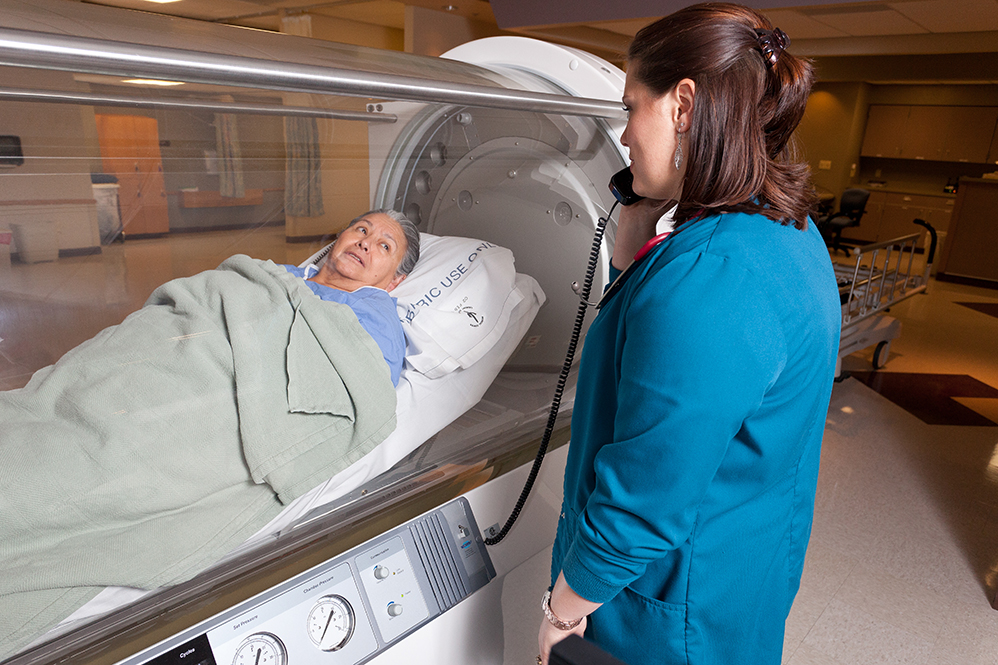
There are various methods of delivering oxygen therapy for wound healing. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves exposing patients to high-pressure oxygen, promoting oxygen dissolution in plasma and enhancing tissue oxygenation. Topical oxygen therapy delivers oxygen directly to the wound using specialized dressings or chambers, promoting healing at the wound site.
Enhanced Angiogenesis and Blood Flow
Oxygen therapy stimulates the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis), which is crucial for supplying nutrients and oxygen to healing tissues. Improved blood flow increases oxygen delivery to the wound area, enabling faster removal of cellular waste products and facilitating tissue regeneration.
Reduction of Infections and Inflammation
Oxygen therapy’s ability to enhance immune cell function and reduce inflammation contributes to preventing and controlling infections in wound sites. Bacteria and pathogens thrive in low-oxygen environments, so providing adequate oxygen levels creates an unfavorable environment for microbial growth.
Promotion of Collagen Synthesis
Collagen is a vital component of wound healing, providing structural support to new tissue. Oxygen therapy promotes collagen synthesis, contributing to the formation of strong, organized tissue that is essential for wound closure and tissue integrity.
Chronic Healing
Oxygen therapy is particularly beneficial for chronic wounds that have difficulty healing due to reduced oxygen levels in the affected area. Conditions like diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers can benefit from enhanced tissue oxygenation, which accelerates healing and reduces the risk of complications.
Collaborative Approach
Effective healing requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals from various specialties. The integration of oxygen therapy into wound care plans should be guided by experienced wound care specialists, who can tailor treatment to the specific needs of each patient.
Conclusion
Oxygen therapy has emerged as a valuable tool in promoting wound healing and tissue repair. By providing the necessary oxygen levels for cellular metabolism, immune function, and tissue regeneration, oxygen therapy enhances the body’s natural wound healing processes. As researchers continue to explore its applications and benefits, oxygen therapy holds the potential to significantly improve the outcomes for individuals with acute and chronic wounds, contributing to faster healing and improved quality of life.