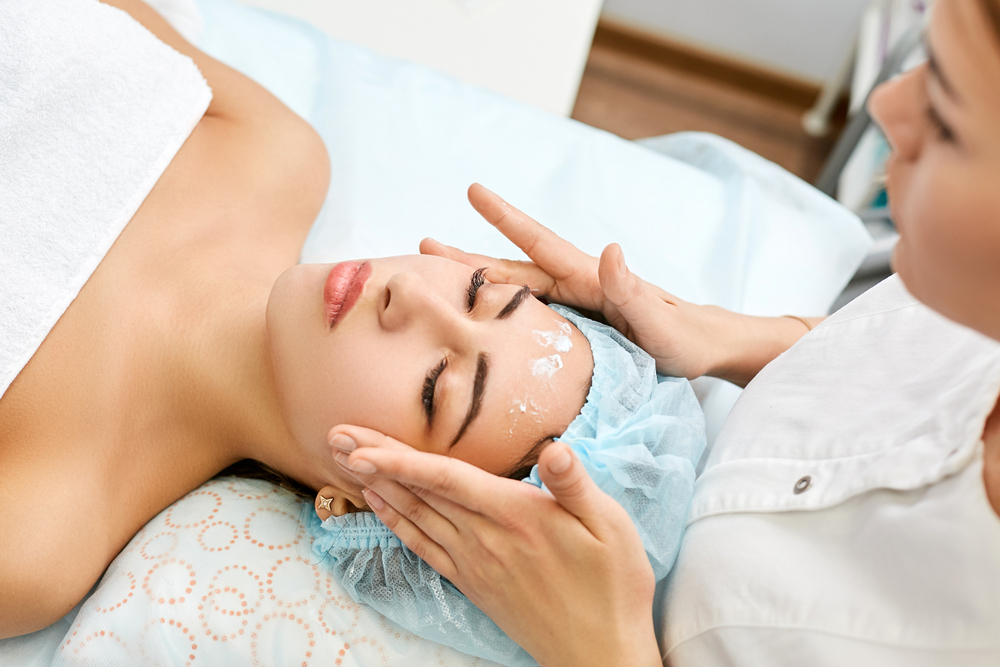
Botox and other injectables, once primarily associated with cosmetic wrinkle reduction, have experienced a remarkable evolution in recent years. These treatments, known for their ability to relax facial muscles and diminish fine lines, are now being explored for an array of innovative medical and cosmetic applications. This essay examines the new and exciting uses for Botox and other injectables, including their application in pain management, treating migraines, improving skin texture, and addressing hyperhidrosis.
Pain Management with Botox
One of the emerging uses for Botox is in the realm of pain management. Studies have shown that Botox injections can effectively alleviate chronic pain associated with various conditions, such as cervical dystonia, myofascial pain syndrome, and neuropathic pain. Botox works by blocking the release of pain-signaling neurotransmitters, providing relief to patients suffering from persistent discomfort. The effectiveness of Botox in pain management has led to its use in treating temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ) and chronic migraines, providing patients with a non-surgical option for pain relief.
Treating Migraines with Injectables
Botox and other injectables have shown promise in treating chronic migraines, a debilitating neurological condition characterized by recurrent severe headaches. Approved by regulatory authorities for this specific use, injections are administered into specific head and neck muscles to reduce the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks. The mechanism by which Botox alleviates migraines is not entirely understood, but it is believed to involve modulating pain signals and reducing muscle tension. This application of Botox has offered significant relief to many migraine sufferers who previously had limited treatment options.
Improving Skin Texture with Injectables
In addition to their wrinkle-reducing properties, injectables have been found to improve skin texture and tone. Some types of injectables, such as hyaluronic acid-based fillers, stimulate collagen production when injected into the skin. This collagen-stimulating effect helps enhance skin elasticity and firmness, leading to smoother and more youthful-looking skin. Furthermore, certain injectables can be used to treat acne scars and reduce the appearance of other facial imperfections, providing patients with a more comprehensive approach to facial rejuvenation.
Addressing Hyperhidrosis with Injectables
Hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating, can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Botox injections have emerged as an effective and minimally invasive treatment option for hyperhidrosis. By blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates sweat glands, Botox can effectively reduce sweat production in the treated areas. This application of Botox has proven particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing excessive underarm sweating, allowing them to regain confidence and comfort in their daily lives.
Conclusion
The new uses for Botox and other injectables have revolutionized the medical and cosmetic fields, expanding the potential benefits of these treatments beyond wrinkle reduction. As research and innovation continue, the applications of these injectables are likely to evolve further, providing patients with increasingly versatile and effective solutions for various medical and aesthetic concerns. From pain management and migraine treatment to skin texture improvement and hyperhidrosis relief, Botox and injectables are contributing to advancements in patient care and quality of life. As with any medical procedure, it is essential to consult with qualified healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable treatment approach for individual needs and goals.