Introduction
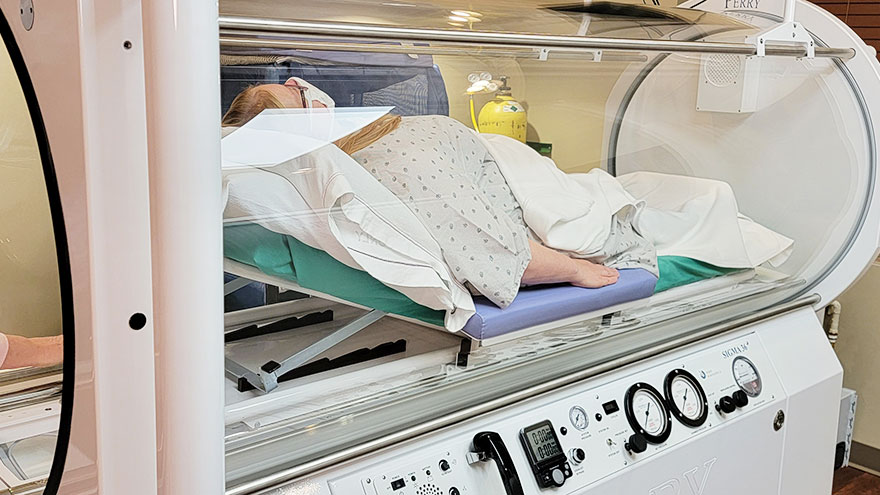
Cardiovascular conditions encompass a wide range of disorders affecting the heart and blood vessels. Adequate oxygen supply is vital for cardiovascular health, as the heart requires oxygen to pump blood and the body’s tissues rely on oxygen for optimal function. Oxygen therapy plays a crucial role in improving oxygenation in patients with various cardiovascular conditions, enhancing their overall well-being.
Importance of Oxygenation in Cardiovascular Health
Healthy cardiovascular function relies on effective oxygenation of the body’s tissues and organs. Oxygen is necessary for the heart’s pumping action, and its deficiency can lead to compromised heart function, reduced exercise tolerance, and a variety of cardiovascular symptoms.
Acute Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)
During a heart attack, a portion of the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen due to reduced blood flow. Oxygen therapy is often administered in acute myocardial infarction cases to increase oxygen delivery to the heart tissue, minimizing damage and supporting recovery.
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
Congestive heart failure is characterized by the heart’s inability to pump blood effectively. Oxygen therapy can help improve oxygen supply to the body’s organs and alleviate symptoms like shortness of breath and fatigue, which are common in CHF patients.
Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension involves high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries, leading to strain on the heart’s right ventricle. Oxygen therapy can help reduce pulmonary artery pressure and alleviate right ventricular strain by improving oxygen levels in the blood.
Cardiogenic Shock
Cardiogenic shock is a severe condition where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. Oxygen therapy supports tissue oxygenation during this critical time, stabilizing the patient while other interventions are initiated.
Post-Cardiac Surgery Care
After cardiac surgery, patients often experience reduced lung function due to anesthesia and limited mobility. Oxygen therapy assists in maintaining adequate oxygen levels during the recovery period, preventing complications and aiding the healing process.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
PAD results in reduced blood flow to the extremities, leading to pain, ulcers, and tissue damage. Oxygen therapy can improve oxygen delivery to affected tissues, promoting wound healing and alleviating pain in PAD patients.
Tailored Oxygen Delivery
Oxygen therapy is tailored to the specific needs of each patient and their cardiovascular condition. The oxygen delivery method, flow rate, and duration are determined based on factors such as oxygen saturation levels, the severity of the cardiovascular condition, and the patient’s overall health status.
Collaborative Care Approach
The use of oxygen therapy in cardiovascular conditions is part of a collaborative care approach. Cardiologists, pulmonologists, and other healthcare professionals work together to determine the appropriate oxygen therapy strategy, considering the patient’s cardiovascular health and overall medical history.
Conclusion
Oxygen therapy plays a crucial role in improving oxygenation for individuals with cardiovascular conditions. By enhancing oxygen supply to the heart, blood vessels, and organs, oxygen therapy supports cardiovascular health, reduces symptoms, and aids in the recovery process. Its tailored approach, guided by healthcare professionals, contributes to improved outcomes and a better quality of life for patients with various cardiovascular conditions.