Introduction
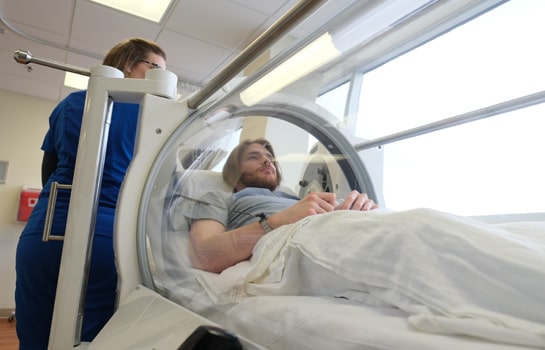
Oxygen therapy is a valuable medical intervention used to treat various conditions and improve oxygen levels in the body. While generally considered safe and well-tolerated, it’s important to understand the potential side effects and safety considerations associated with oxygen therapy to ensure its appropriate use.
Common Side Effects
Most individuals tolerate oxygen therapy without significant issues. However, some common side effects may include nasal dryness, irritation, and discomfort. The high flow of oxygen can lead to drying of the nasal passages, which can be alleviated with the use of humidified oxygen or saline nasal sprays.
Oxygen Toxicity
Excessive oxygen exposure over a prolonged period can lead to oxygen toxicity, a condition that can cause lung damage and other adverse effects. This is particularly a concern when using high-flow oxygen for extended durations. Healthcare providers closely monitor oxygen levels to prevent oxygen toxicity, especially in patients on long-term oxygen therapy.
Suppression of Respiratory Drive
In some cases, receiving high levels of oxygen for extended periods can suppress the body’s respiratory drive, leading to hypoventilation. This is more common in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or other respiratory conditions. Monitoring oxygen saturation levels and adjusting oxygen therapy accordingly helps prevent this issue.
Fire Hazard
Oxygen supports combustion, making it a potential fire hazard. Patients using oxygen therapy should avoid smoking and keep oxygen away from open flames, sparks, and flammable materials. Oxygen equipment and containers should be kept in well-ventilated areas and stored safely.
Nasal and Sinus Discomfort
Patients using nasal cannulas or masks may experience discomfort over time due to pressure or friction on the skin. Proper fitting and adjustments can help minimize this issue. Patients with pre-existing sinus or ear problems might also experience worsened symptoms.
Dependency Concerns
Long-term oxygen therapy might lead to a psychological dependency on oxygen, with some patients feeling anxious when not using it. Healthcare providers work with patients to ensure they understand the appropriate use of oxygen therapy and address any concerns they may have.
Interaction with Smoking
Using oxygen therapy while smoking increases the risk of fire and can compromise the therapy’s effectiveness. It’s crucial for patients to refrain from smoking while using oxygen and to follow healthcare provider recommendations for smoking cessation.
Individualized Assessment
The safety and side effects of oxygen therapy depend on factors such as the patient’s underlying condition, the type of oxygen delivery system used, and the duration of therapy. Healthcare providers conduct thorough assessments to determine the appropriate oxygen flow rate and therapy duration for each patient.
Conclusion
Oxygen therapy is generally safe and well-tolerated when used as prescribed by healthcare professionals. While potential side effects and safety considerations exist, healthcare providers closely monitor patients to prevent issues such as oxygen toxicity and respiratory suppression. Patients should work closely with their healthcare team to ensure safe and effective oxygen therapy, minimizing the risk of adverse effects and maximizing the benefits of improved oxygenation.